How the ISSB is revolutionizing sustainability reporting


Sustainability has become a pressing concern for businesses and organizations of all sizes. Investors, stakeholders, and the public increasingly demand transparency and accountability regarding sustainability practices. In response to this demand, the ISSB was established to unify sustainability reporting, reduce the burdens, complexity, and confusion faced by companies, and encourage wider adoption of sustainability practices. In this blog post, we’ll take a closer look at the ISSB framework, its key features, and how it can help organizations demonstrate their commitment to sustainability and promote transparency and accountability.
The International Sustainability Standards Board (ISSB) was created by the International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) Foundation in November 2021 at the UN Climate Change Conference (COP26). The aim is to provide a global baseline of sustainability disclosures that align with the requirements of capital markets. While several frameworks, principles, and standards already exist, the current reporting landscape is fragmented and inconsistent – making it challenging to make clear and concise comparisons across the global landscape. Recognizing this challenge, ISSB has collaborated with stakeholders from existing disclosure frameworks, international government bodies, and corporate representatives to create a global baseline. The ISSB has international support backed by the G7, the G20, the International Organization of Security Commissions (IOSCO), the Financial Stability Board, African Finance Ministers and Finance Ministers, and Central Bank Governors from more than 40 jurisdictions.
The ISSB has four key objectives:
Drawing on the success of market-led investor-focused reporting initiatives like the Climate Disclosure Standards Boards (CDSB), the Task Force for Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD), the Value Reporting Foundation’s Integrated Reporting Framework, the industry-based SASB Standards, and the World Economic Forum’s Stakeholder Capitalism Metrics, the ISSB has built upon these efforts to develop globally accepted sustainability reporting standards.
The ISSB is dedicated to producing standards that are not only cost-effective but also decision-useful and market-informed. With efficiency in mind, the standards have been designed to help companies report what is necessary globally to investors across markets. Additionally, the standards aim to provide the appropriate information in a manner that supports investors' decision-making and enables international comparability to attract capital.
Using the ISSB standards for sustainability disclosure offers several benefits, including:
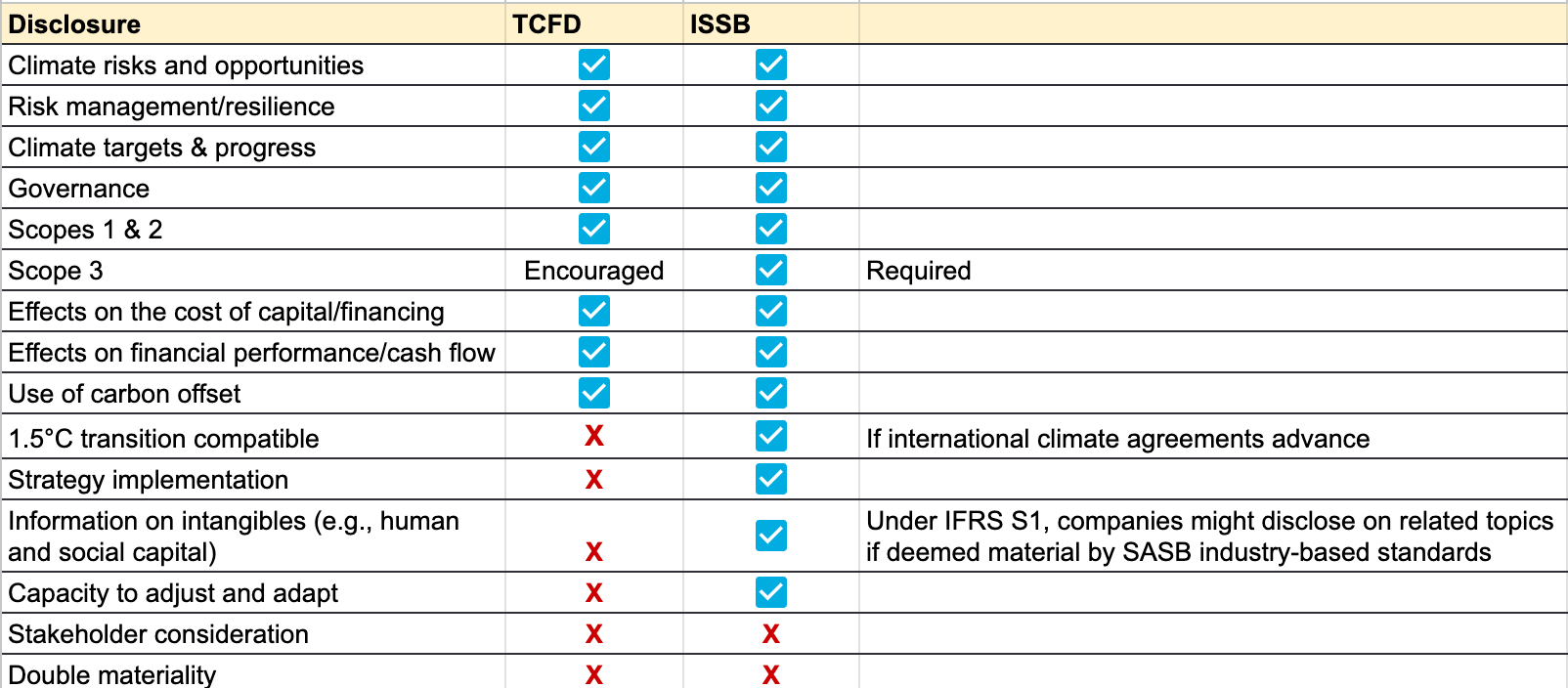
The ISSB has published two exposure drafts for stakeholder input in July 2022 and is currently reviewing and considering all feedback and comments received on IFRS S1 General Requirements for Disclosure of Sustainability-related Financial Information (PDF) and IFRS S2 Climate-related Disclosures (PDF). The proposed IFRS S1 draws on sector-specific Sustainability Accounting Standards Board (SASB) standards.The IFRS S2 are consistent with the Taskforce on Climate related Financial Disclosures (TCFD) and focuses on four key areas: governance, strategy, risk management, and metrics and targets.
IFRS S1 lays the groundwork and basis for the ISSB to develop additional specific standards on various sustainability topics in the future. It mandates that companies must disclose relevant information about all significant sustainability-related risks and opportunities that may impact their enterprise value and require assessment by investors. Additionally, by incorporating the SASB industry-specific approach, the ISSB acknowledges that sustainability concerns differ across industries. The ISSB has confirmed that companies must take into account the sector-specific SASB standards, disclosures, and metrics to meet the IFRS S1 requirements effectively, while also being able to consider the Climate Disclosure Standards Board (CDSB) guidance. The ISSB has brought together all SASB and CDSB materials under one roof, providing companies with a single source of reference.
The disclosure requirements stated in IFRS S2 are in agreement with the 11 recommended disclosures and four thematic pillars of the TCFD, which is positive considering the TCFD has support from more than 2,600 global advocates, including over 1,000 financial institutions. While mostly aligned with the TCFD, the IFRS S2 requires additional and more granular information from reporting entities.
New announcements and developments in sustainability reporting seems to be made almost daily, including:
Whether the ISSB standards become adopted worldwide and which specific companies must apply them are subject to the discretion of each individual national regulator and authorities to decide. The ISSB intends to issue the final version of IFRS S1 and S2 in 2023. Its goal is to foster greater consistency and alignment between other standards, promote greater acceptance, reduce the complexity and burden of sustainability reporting, and promote greater uptake.
29-June-2023: The International Sustainability Standards Board (ISSB) has officially launched its global sustainability and climate disclosure standards IFRS S1 and IFRS S2. To learn more, visit: What the new ISSB global sustainability and climate disclosure standards mean for your business.